- BTI Group
- IT Products Services Articles
- 5 min read
What Is Network Design? Best Practices for Business
What is Network Design?

Steps to Create an Efficient Network Design
Inventory of Network Assets
- Endpoints: Computers, laptops, tablets, servers, etc.
- Users: Employees, contractors, guests
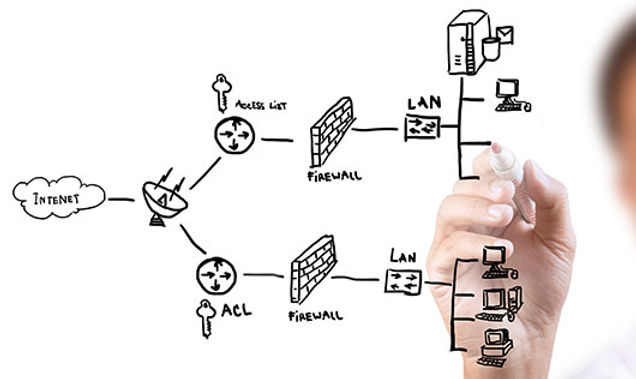
- Devices: Routers, switches, servers Local Area Networks (LANs)
- Security Tools: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems
Visualizing and Diagramming the Network
Redesigning an Existing Network
How to Design a Network: Key Considerations
Identify Business Needs and Requirements
Analyze Your Existing IT Infrastructure
Create a Network Diagram
Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Maintain Proactive Network Support and Maintenance
Test your Network
Implement Proactive Monitoring
Utilize network monitoring tools to detect and address issues before they escalate. BTI services such as Remote Monitoring & Management as a Service (RMMaaS) and GlobalView Support are designed to ease the burden of network monitoring and management while you focus on business. If you would like to know more about RMM as a Service, click here!
Best Practices in Network Design
Keep It Simple
Scalability
Redundancy
Integrated Security
- Access Controls: Use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based permissions to restrict network access.
- Firewalls: Act as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks, filtering traffic based on defined rules.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Monitor traffic for suspicious activity and block potential threats.
- Secure Data Handling: Use encryption, data loss prevention, and regular backups to protect sensitive information.
Modular Design for Simplified Management
Performance Optimization
Consistent Policies
Did you know that 95% of data breaches are caused by human error? Standardizing network and security policies across your organization enhances efficiency and compliance. For instance, enforcing consistent password requirements strengthens security and reduces administrative overhead.
Comprehensive Documentation
Continuous Monitoring
Implement continuous monitoring to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. Services like BTI’s RMM as a Service and GlobalView Support can streamline your monitoring process while enabling you to concentrate on business profitable tasks while we proactively monitor your network 24/7/365
Security Measures in Network Design
Firewalls and Access Controls
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Secure Protocols and Data Encryption
Employee Education and Regular Audits
Network Monitoring and Analysis
Advanced Network Design Technologies
Network Virtualization and SDN
Quality of Service (QoS) and Traffic Prioritization
Conclusion: Keys to a Successful Network Design
Here at BTI, we have 35+ years of experience helping our clients create the perfect network design plan for your specific business needs. Are you ready to take your network to the next level?
Contact BTI today to schedule your FREE business assessment and experience world class network design.