What is WAN? The Ultimate Guide for Businesses
Ensuring seamless communication and data accessibility across multiple locations is crucial for the success of any multi-site enterprise. This guide explores what WAN (Wide Area Network) is and how WAN networks can benefit multi-site businesses looking to enhance their network performance across all locations.
Before we start, it is important that you understand the difference between WAN and LAN (Local Area Network).

What is WAN?
A WAN is a large network that connects computers and devices over a wide geographical area, like across cities, states, or even countries. It allows various locations, such as office branches, to communicate and share information with each other.
What is LAN?
LAN is a smaller network that connects computers and devices within a limited area, like within a single building or office. It allows devices like computers, printers, and servers to communicate and share resources quickly and easily.
What is WAN Connectivity Used For?
Wide Area Network (WAN) connects multiple locations, employees, and resources within each other enabling businesses to share vital business information regardless of location. This allows multi-site and cloud-based businesses to:
-
Improve business communications and resource sharing across multiple locations.
-
Give access to secure data storage and ensure data is backed up remotely.
-
Efficiently run cloud-based applications while supporting remote work.
-
Run and support internal business applications efficiently.
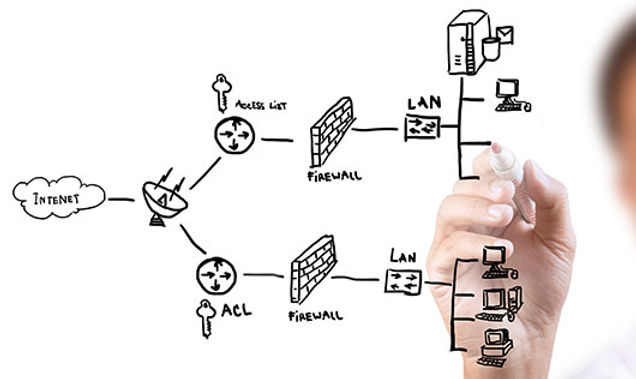
What is a WAN Router?
A WAN router (also called edge or border router) is the device in charge of directing your network traffic across various locations within your wide area network. Its main job is to connect your internal network to your internet providers’ network while ensuring data travels seamlessly and efficiently.
What are WAN protocols?
WAN protocols are the rules that govern how data is going to be transmitted and communicated across a network over long distances. There are 4 main wide area network protocols:
-
Frame Relay
-
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
-
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
-
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
Frame Relay
Frame relay is the oldest technology used to transmit data over a network. Frame relay packages data into smaller units called “frames” and sending data through a private line to a connection point in the network known as “frame relay node”
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Instead of transforming data into frames, ATM formats data into small, fixed units called “cells.” Each cell contains 53mb of data. Once data is divided into a “cell,” it is sent through the network and then rearranged at the destination making ATM technology useful for voice and video transfer.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
An MPLS directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses. MPLS can handle a variety of protocols, making it versatile for routing and traffic engineering.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN (Software Defined WAN) is a virtual architecture that leverages software to connect LANs (Local Area Network) across long distances. By leveraging tools like virtualization, network overlay, and the ability to create application-level policies allows SD-WAN to:
-
Reduce operational costs
-
Improve data transfer
-
Simplify network management and increase efficiency
How Does Wide Area Networks (WAN) Works?
As previously mentioned, a Wide Area Network (WAN) allows organizations to connect their resources across multiple locations, whether those resources are in on-premises data centers, branch offices, or virtual private clouds (VPCs).
Building a private network across vast geographic areas is impractical and expensive, most companies rent network infrastructure from third-party service providers. Here’s how distinct types of connections work within a WAN:
Leased Lines
A leased line is a dedicated, direct connection between two LANs (Local Area Networks) that a company can rent from a large network provider like internet providers.
How Leased Lines Work
Leased lines provide a reliable and private connection, but they may not always be physical cables. Sometimes, they are virtual connections set up by the service provider over their existing network infrastructure.
Tunneling
Tunneling is a technique used to securely send data over the public internet by encrypting it and encapsulating it within another data packet.
How Tunneling Works
When you use tunneling, you create a Virtual Private Network (VPN) that allows you to send encrypted data from one location to another as if they were on the same private network allowing you to ensure security and privacy while using the public internet.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
MPLS is a method for speeding up network traffic by routing it based on labels rather than long network addresses.
How MPLS Works:
MPLS directs data along the most efficient path across a network by using predefined labels, which helps improve performance, especially for critical applications.