- BTI Group
- IT Products Services Articles
- 7 min read
Wireless Network Design: How to Create the Perfect Wi-Fi Plan

The Basics of Wireless Network Design
What is Wireless Network Design?
Wireless network design is the process of creating, planning, and configuring your business wireless network to meet your business-specific security, performance, and coverage needs.
Why is Wi-Fi Planning Important?
Nowadays, your Wi-Fi can be considered a fuel that drives your business forward. Today’s communication systems, applications, and everyday work-related tasks are network-dependent. The moment Wi-Fi fails, everything grinds to a halt.
“Network downtime costs an average of $5,600 per minute.” – Gartner.
“More than 2/3 of outages cost over $100,000.00” -Uptime Institute

Crafting Your Wireless Network Design Strategy
8 Steps for Effective Wi-Fi Planning
The best practices to wireless network design include:
Business Requirements
Conduct a Site Survey
Optimize to Meet your Capacity Needs
Prioritize your Devices Following the LCMID Method
Radio Frequency Requirements
Evaluate your Physical Environment
Evaluate your Building Materials to Eliminate Interference
Measure RF Activity
Security Requirements
Create Security Policies
Implement the Appropriate Cybersecurity Measures
Business Requirements
- How many devices will require access simultaneously?
- What are the key devices that need to always have a connection?
- How does “good Wi-Fi” look like for you and your specific needs?
Conduct a Site Survey
Optimize Your Network to Meet Your Capacity Needs

Prioritize your Devices Following the LCMID Method
Radio Frequency Requirements
- Ceiling Height: How tall are the ceilings in the areas needing coverage?
- Access Point Installation: Can access points be conveniently mounted given the available access?
- Wall Composition: What materials are the walls made from?
- Network Noise: How much interference comes from neighboring networks?
Evaluate Your Physical Environment

Evaluate your Building Materials to Eliminate Interference
Measure RF Activity
- Explore Your Electromagnetic Environment: Just like fish in the sea, your Wi-Fi signals move through an ocean of electromagnetic waves. Understanding what other signals are in the area while appropriately spacing your devices between each other can help you avoid Wi-Fi “traffic jams.”
- Choose the Right Channel: Think of each Wi-Fi channel as a lane on a highway. Some lanes (channels) are busier than others, especially in crowded urban areas. Picking the less congested one keeps your Wi-Fi moving fast.
- Be Aware of Radar Activity: When radar signals cross paths with Wi-Fi networks, the result can be a bit like two radio stations interfering with each other—it can mess things up! Specifically, radar waves can interfere with Wi-Fi signals, especially if both are using the 5 GHz frequency band. This might limit the channels your Wi-Fi can use, making it less efficient. Imagine your Wi-Fi is a car that suddenly finds many roads closed and must keep detouring; naturally, it’s going to slow down. Similarly, if your Wi-Fi access points (APs) keep jumping channels to dodge radar signals (a process called Dynamic Frequency Selection, or DFS), your network’s performance could drop, leading to annoying delays and buffering when you’re online.
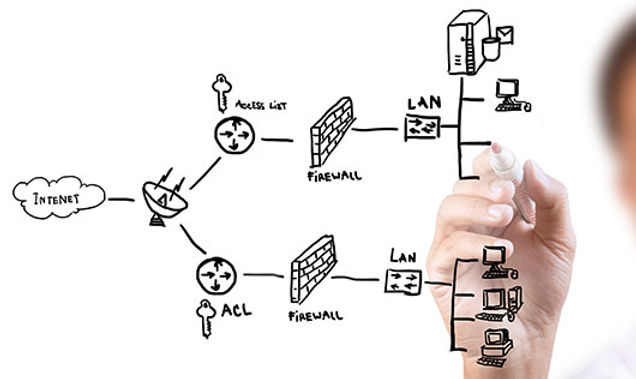
Security Requirements
Create Security Policies
- Mitigate risks
- Meet your industry compliance requirements.
- Create and maintain a strong cybersecurity culture within your workplace.
Implement the Right Cybersecurity Measures
- Encryption
- Role-based access control vigilant guards
- Firewall
- Traffic monitoring
- Cutting-edge defense systems
- Advanced threat protection
Conclusion
FAQ's
- Planning
- Designing
- Site Surveying
- PAN (Personal Area Network),
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- LAN (Local Area Network)